Securing communication across distributed environments requires more than just strong cryptography, it also demands agility, programmability, and centralized control. Centrally Controlled IPsec (CCIPS) introduces a new way to deploy and manage IPsec tunnels by combining SDN principles with the I2NSF (Interface to Network Security Functions) standard.
What is CCIPS?
Traditional IPsec deployments rely on IKE (Internet Key Exchange) for tunnel negotiation. While robust, IKE can be complex to manage at scale, especially in dynamic environments. CCIPS takes a different approach: it defines an IKE-less model where a central controller provisions, manages, and monitors IPsec tunnels across the network.
This model leverages I2NSF IPsec specifications to provide:
-
Standardized interfaces for setting up security functions (e.g., VPNs, firewalls)
-
Centralized policy enforcement and lifecycle management of tunnels
-
Application-driven deployment of secure communication channels
-
The result is a flexible and interoperable framework for secure networking in modern architectures.
How it works?
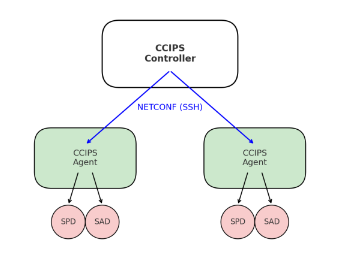
The CCIPS architecture is built around two main roles:
CCIPS Controller
The central component that manages requests from applications. Translates high-level security requirements into tunnel configurations based on the IKE-less data model. Manages the lifecycle of tunnels via YANG notifications, ensuring that tunnels are created, monitored, and removed correctly.
CCIPS Agents
Network devices capable of terminating one end of an IPsec tunnel. Receive configuration parameters directly from the controller. Deploy the requested tunnels, enforce security policies, and report status updates. Generate notifications back to the controller for lifecycle management.
Why this matters
The CCIPS architecture provides significant advantages over traditional IKE-based deployments:
Centralized control: Policies and lifecycle management are coordinated through a single controller.
Scalability: Simplifies deployment in multi-cluster or multi-domain environments.
Interoperability: Built on I2NSF standards, ensuring consistency across different implementations.
Auditability: Lifecycle events and tunnel operations are logged and verifiable.
In short, CCIPS modernizes IPsec by making it programmable, centrally managed, and lifecycle-aware, an essential step toward secure and agile communication infrastructures.

